Keyword [Multi-task Learning]
Zhao W, Wang B, Ye J, et al. A Multi-task Learning Approach for Image Captioning[C]//IJCAI. 2018: 1205-1211.
1. Overview
In this paper, it proposes Multi-task Learning Approach for Image Captioning (MLAIC)
- multi-object classification model. regularize CNN encoder
- syntax generation model
- image captioning model. benifit from object categorization and syntax knowledge
2. Architecture

2.1. Ground-Truth
2.1.1. Object Vector

- 1 is present.
- C. the number of categories
2.1.2. Image Description

- T. sentence length
2.1.3. Combinatory Category Gramma (CCG)

2.2. Shared CNN Encoder
- image to L vectors (HxWxC–>LxD)
- L=14x14, D=2048

- shared CNN encoder fine-tuned with both captioning and classification
2.2.1. Classification
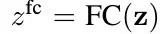
2.3. Shared LSTM Decoder
- LSTM_1. top-down visual attention model
- LSTM_2. language model
2.3.1. LSTM_1
- Input.

- z. image mean feature
- e^w. previously generated word embedding
- e_s. previously generated syntax embedding
- h^(2). previously output of LSTM_2
- Output.

2.3.2. ### LSTM_2
- Input

sigma. feed-forward NN
- Output

2.4. Multi-Task Learning
classification. multi-label margin loss

other two task. NLL

- All

3. Experiments
3.1. Details
- λ1 = 0.2, λ2 = 0.7, λ3 = 0.1
- LSTM_1 = 1000 unit, LSTM_2 = 512 unit
- word embedding = 512, CCG supertag embedding = 100
- beam size = 5
3.2. Comparison

3.3. Ablation

